
One last thing: since we do have an ion, we should put brackets around the structure and put a negative sign on the outside to show that it is an ion. That makes sense, though, because we have a negative one up here so it needs to match our Lewis structure for HCO2. If we check the formal charges, we'll see that all the atoms have a formal charge of zero except this Oxygen right here. So we've used all 18 valence electrons, and each of the atoms has its outer shell full. The above calculation is exposing that this large size ion has a net charge of -1. Formal charge of other two oxygen (7-6-(1/2)) 0.5. The Oxygen, it still has eight valence electrons but now the Carbon, it has eight valence electrons. Formal charge of Oxygen with negative charge -1. Sometimes one Lewis Structure is not Enough Some molecules or ions cannot be adequately described by a single Lewis structure. Use formal charges to determine major and minor resonance contributors. So we're still using 18 valence electrons. Learning Objectives Use resonance structures to show electron delocalization.

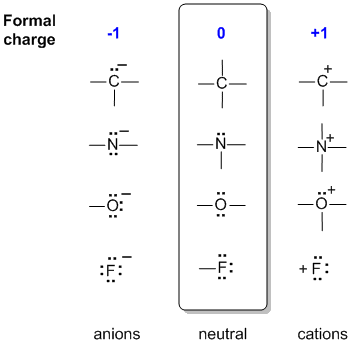
Formal charges can help identify the more important resonance structures, that is, hitherto we have treated all resonance structures as equal, but this.
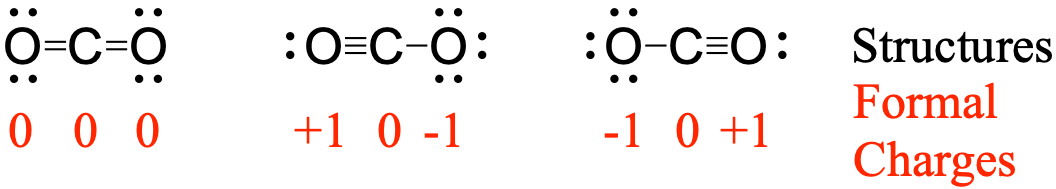
Let's take these two valence electrons and move them to the center to form a double bond. The sum of the formal charges of all the atoms in a neutral molecule equals zero The sum of the formal charges of all the atoms in an ion equals the charge of the ion. However, the Carbon only has six, so we're going to have to share some electrons to get Carbon to have an octet. Write the formal charges on all atoms in BH4 BH 4. In this case, the sum of the formal charges is 0 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 1+, which is the same as the total charge of the ammonium polyatomic ion. Complete answer: - In the question it is asked what the formal charge of CO is. Adding together the formal charges on the atoms should give us the total charge on the molecule or ion.
#FORMAL CHARGE OF CARBON FULL#
The Oxygens have eight valence electrons, so their octets are full, and the Hydrogen has two valence electrons, so it has a full outer shell, as well. Hint: The formal charge of the atom in a polyatomic molecule is going to depend on the number of electrons gained from other atoms or donated to other atoms.The formal charge of the atom in the molecule will be positive or negative or neutral. So at this point, we've used all 18 valence electrons. We'll put two between atoms to form chemical bonds, and we'll go around the outside. We have a total of 18 valence electrons for the HCO2- Lewis structure. Carbon is less electronegative than Oxygen, so we'll put a Carbon in the center, and then we'll put the Oxygens on the Carbon. Hydrogens always go on the outside of Lewis structures. Polar Bonds - In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.Transcript: For the HCO2- Lewis structure, we have a total of 18 valence electrons.Hydrogen Bonds - It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge In a Lewis structure of the compound, the carbon has a formal negative charge.Covalent Bonds - Compounds that contain carbon commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding. In each of them, the formal charge on the center carbon is 0, the double bonded oxygen is 0, and the two single bonded oxygens are each -1. Formal Charge Formula: You can calculate the formal charge of any atom with the help of the equation below: F C V ( L P + 0.5 B E) Where: FC Formal Charge on Atom. Another compound that has a triple bond is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ), whose Lewis diagram is as follows: Example 4.4.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
